Approval of insect species for food helps cook up new dishes, product offerings

Editor's note: In this weekly feature China Daily gives voice to Asia and its people. The stories presented come mainly from the Asia News Network (ANN), of which China Daily is among its 20 leading titles.
Fancy some lychee balls with crispy chili crickets or sushi with superworms?
The Singapore Food Agency said on July 8 that it has approved 16 species of insects for consumption.
The insects include various species of crickets, grasshoppers, locusts, mealworms and silkworms.
For industry players in Singapore who have been gearing up for this moment by experimenting with and developing new insect-based recipes and products, the approval is a long-awaited one.
READ MORE: Silkworm sashimi, cricket curry on menu
The food agency began public consultations on the possibility of allowing 16 species of insects for consumption in 2022, The Straits Times reported then.
Insects have been touted by the UN Food and Agriculture Organization as a more sustainable alternative to meat, as they have high protein content and produce lower greenhouse gas emissions when farmed.
In April 2023, the food agency said it would give the green light for these species to be consumed in the second half of 2023. This deadline was later pushed to the first half of 2024.
At least two industry players — Singapore-based Future Protein Solutions and Asia Insect Farm Solutions — have decided to call it quits, as the long wait had thrown their business viability into question.
But other groups are persisting with their insect offerings.
Altimate Nutrition and House of Seafood, for instance, hope to roll their products out to the mass market.
Other enterprises are taking it slow, hoping to introduce insects into consumer diets gradually, such as by incorporating insect powder as an ingredient in protein bars.
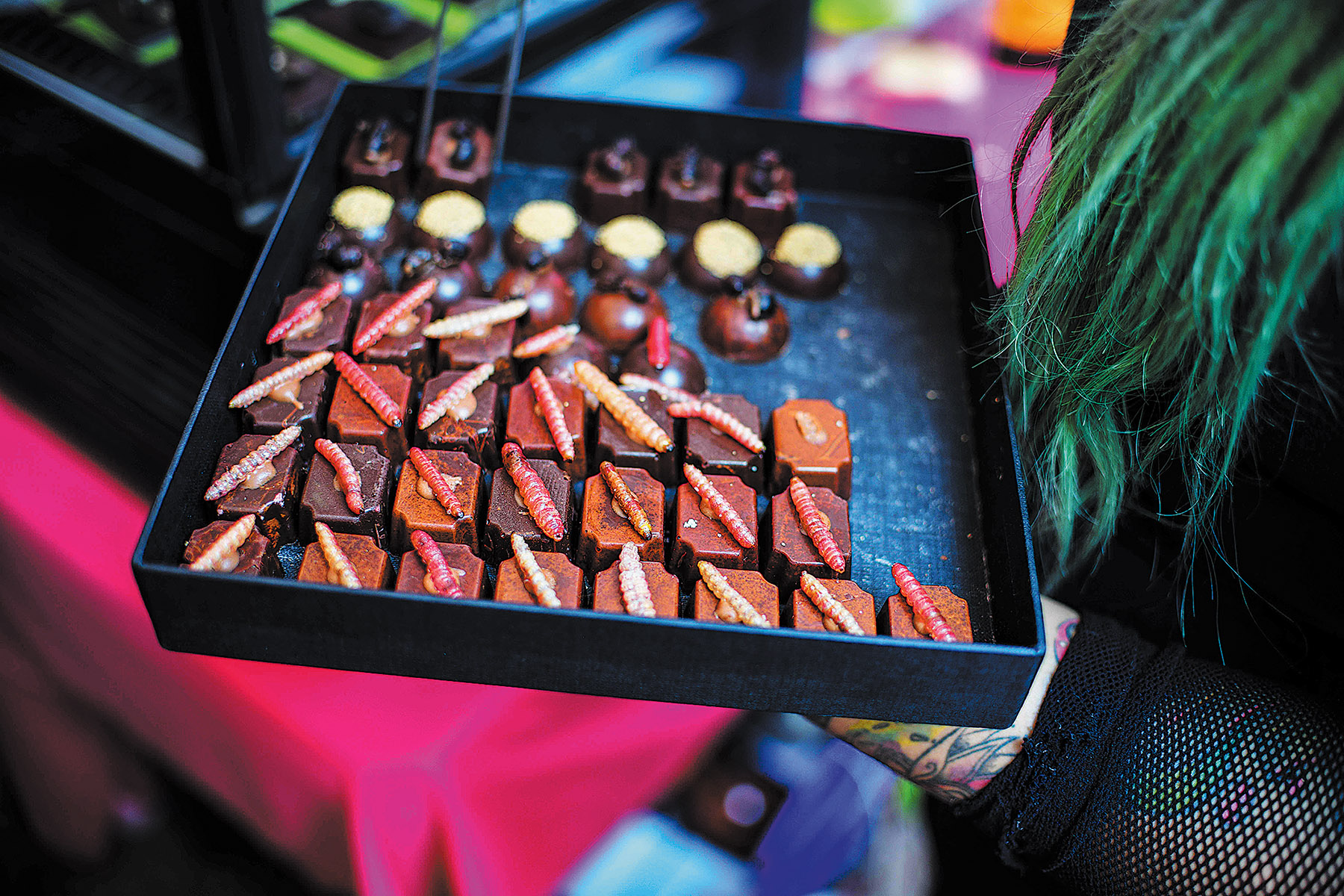

Whetting appetites
Francis Ng, House of Seafood restaurant's chief executive, is cooking up a menu of 30 insect-infused dishes to give customers more choice.
Of the 16 approved species, the restaurant will add superworms, crickets and silkworm pupae to some of its seafood dishes, such as salted egg crab.
Prior to the approval, the restaurant had been getting five to six calls daily inquiring about its insect-based dishes, Ng said.
"Many of our customers, especially young people who are under 30 years old, are very daring. They want to be able to see the whole insect in the dish," he said.
Ng anticipates that sales from insect-based dishes will increase his revenue by about 30 percent.
Javier Yip, founder of logistics company Declarators, has set up another business and secured a license to import insects from farms in China, Thailand and Vietnam for sale in Singapore.
He will sell a range of bug snacks under the brand name InsectYumz. Several types of insect snacks will be available for a start, including original and tom yum-flavored crickets and mealworms. There will also be cricket powder, which is a protein powder.
These items will soon be listed on his website and other e-commerce sites, as well as supermarkets and restaurants, he said.
Asked why he decided to venture into importing insects, Yip said: "I enjoy eating them; in fact, the first time I tried an insect was at a shop in Tampines (a region in Singapore) in the 1990s."
As he runs a logistics company, Yip feels he has the know-how and ability to import these insects into Singapore. He hopes to provide such snacks to those who might enjoy them, particularly young people.
Altimate Nutrition, which creates insect food products for humans, has sought to garner interest among younger people by educating consumers over the years.
Its main product offerings are cricket-infused protein bars, which come in a range of flavors, from strawberry to banana chocolate.

While waiting for regulatory approval, the company conducted workshops and educational sessions at almost a hundred schools, from preschools to institutes of higher learning, said its co-founder, Hiew Yuen Sheng.
"During our workshops, we targeted mostly young people who may be more adventurous when it comes to trying insects, and we educated them on the benefits of insects as a more sustainable protein source," he said.
Surveys conducted after the program found that about 80 percent of students polled would be willing to try the insects after they are approved, he said.
Altimate Nutrition is hoping to launch its cricket protein bars at eco-friendly store Green Collective as soon as possible, to be the "first movers", Hiew said.
It is collaborating with various food and beverage players — it supplies House of Seafood with some of its bugs and is working with Origin Bar to launch a cricket-based cocktail.
To carry out more research and development, Altimate Nutrition has formed a joint venture named ProteinInnovation with its supplier, Thai insect farm Global Bugs.
ProteinInnovation will look into growing crickets in the most productive, cost-effective way and the collaboration will help Global Bugs to better tap the Singapore market, said Global Bugs co-founder and chief executive Kanitsanan Thanthitiwat.
"While there are many cricket farms in the Thai market, the challenge lies in determining who can produce the largest volume of crickets and in the most cost-effective way," she said.
ProteinInnovation will be raising funds to build another high-tech cricket farm in Thailand, which is capable of growing about 200 metric tons of crickets a year — 20 times more than its current capacity.
The crickets will be bred, using automation, in little "boxes", to alleviate manpower costs, and being modular, these can easily be scaled up, she said.
Other companies are waiting to test consumer reception before deciding on their launch plans.
Aaron Chen, the chief executive of Werms, which currently sells insects such as crickets and mealworms as pet food, is waiting to see if there is any consumer demand for his insects, before deciding to offer them for human consumption.
While these insects are grown in a similar way — whether for humans or for pets — greater biosecurity measures will be needed if they are to be sold for human consumption. A new farm will also have to be set up to prevent cross-contamination, for example, and a new license will be needed.
"While we can scale up rather quickly, there might be quite a bit of costs involved for us to venture into the edible insect market, so we'll wait and see what happens," he said.
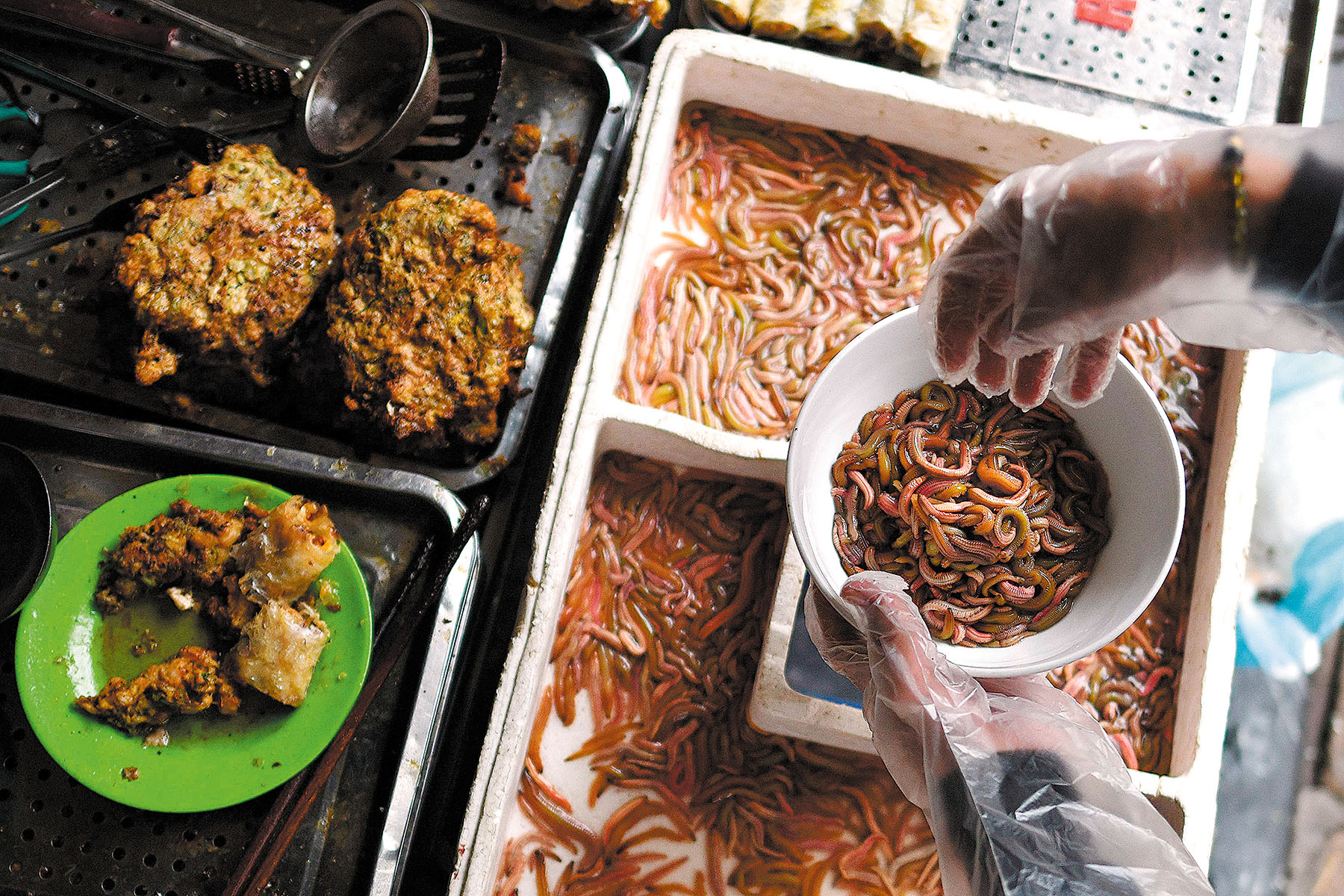

Tasting ground
Japanese startup Morus is looking to launch a range of silkworm-based products in Singapore, targeting high-end restaurants and consumers, as they are high-income and health conscious, said Ryo Sato, its chief executive.
Its products include a pure silkworm powder — which can be used as a food ingredient — along with matcha powder, protein powder and protein bars.
Given that Singaporean consumers do not have a history of consuming insects, Morus will also conduct more pop-up events and consumer workshops, Sato said.
ALSO READ: Diners relish insects in their diets
Once it is able to scale up and reduce costs of production, Morus will start focusing on the mass market, he said.
The Singapore Food Agency said that those intending to import or farm insects for human consumption or livestock feed must meet its guidelines, which include providing documentary proof that the imported insects are farmed in regulated establishments with food safety controls and are not harvested from the wild.
Insects not on the agency's list of 16 will have to be evaluated to ensure that the species are safe for consumption, it said.
Companies selling pre-packed food containing insects will also have to label their packaging as such, so that consumers can make informed decisions on whether to purchase the product.
Insect products will also be subject to food safety testing. Those that do not meet agency standards will not be allowed for sale.